The Factors Behind Complications of Diabetes
Authors: Janet Worsley Norwood and Charles B. Inlander
Excerpt from: Understanding Diabetes
Generally, you can't tell diabetic complications are developing, at
least not without undergoing tests or medical procedures in a doctor's
office. Diabetes proceeds unnoticed, silently ravaging the body. You
might be without symptoms until some damage is already done.
There is, however, one surefire indication that problems are
developing: persistently high blood-sugar levels. Diabetes experts
believe that over the long haul levels above 240 mg/dl are unacceptable
and dangerous. However, the ideal level for you is the target set by you
and your physician. It will probably be in the 80 to 120 mg/dl range.
The length of time a person has diabetes also comes into play when
looking at complications. Because people with type 1 diabetes usually
get the disease earlier in life than those with type 2, they have the
dubious distinction of running a greater risk of developing
complications than those with type 2. For the most part, complications
appear in people who have had diabetes for fifteen years or more,
although certain short-term complications can appear (and disappear) at
any time. Evidence of diabetes-related eye problems, for example, is
present after five years in 1 percent of type 1 cases; by fourteen
years, the percentage is close to 100.
The type of complications that develop also depends on diabetes type.
Individuals with type 1 tend to develop different problems than those
with type 2. For instance, type 1 diabetes tends to produce vision
problems sooner than does type 2 diabetes, while type 2 diabetes appears
to be linked to more heart attacks and strokes. The rates at which
complications proceed also vary wildly.
Scientists don't really know why these differences exist. Nor do they
know why complications sometimes develop in people who have blood-sugar
levels firmly in hand while other people never develop complications,
regardless of how well or how poorly they control their blood sugar. It
may boil down to genetic differences or even to factors yet unknown.
The thing to remember is that everyone has different responses to
high and low blood sugar, so you may want to know what their symptoms
tend to be. Self-monitoring of blood glucose can track sugar patterns
and guard against these short-term, but potentially deadly,
complications.
Long-Term ComplicationsLong-term, chronic
complications differ from short-term complications in that they take
more time in developing, and once they arrive are less likely to
disappear. Many long-term complications are tied to those structures
that distribute blood throughout the body; the small and large blood
vessels. Although scientists are not certain how it happens, they think
that years of carrying blood with high sugar levels eventually damages
or impairs blood vessels. The faulty metabolism of someone with diabetes
may also create some chemical change that makes blood vessels more
vulnerable to damage. Either way, many diabetic complications are
vascular complications--complications pertaining to blood vessels, in
other words.
Let's look now at some of the major long-term complications faced by people with diabetes.
EYE PROBLEMS
Eye problems that diabetes might cause include minor problems in
focusing, premature development of cataracts, and various degrees of
retinal damage (otherwise known as diabetic retinopathy).
If you have diabetes, it's very likely that you will experience at
least one of these problems in the course of your lifetime. Most people
who have had diabetes for five to ten years show some signs of eye
damage, although it may be slight.
Cataracts
A cataract, a clouding of the lens in the eye, is a very common
problem in older people, including folks who don't have diabetes.
However, the evidence suggests that diabetes accelerates cataract
development. The hastened development is thought to be a result of the
intricate and still incompletely understood relationship between high
blood-sugar levels and aging. One popular theory posits that when people
have diabetes for an extended period of time, sugar by-products begin
to build up in the lens of the eye, eventually leading to cataracts.
Mild cataracts are often left as they are--but an individual with
diabetes is encouraged to work at keeping blood-sugar levels within the
normal range, which seems to slow the accumulation of sugar by-products
and, thus, slow the progression of complications. Once severe cataracts
develop, however, many ophthalmologists believe that the best course of
action is to remove the cataract and replace it with an artificial lens,
also known as an intraocular lens. This surgical procedure can be done
right in a doctor's office. Although cataracts certainly impede good
vision, they are less troublesome than another long-term complication,
diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy means damage to or disease of the retina, the
delicate membrane that lines the inside wall of the eye. The retina
responds to light and receives the image formed by the lens. When it
becomes seriously damaged, blindness may result. In fact, retinopathy is
the most frequent cause of vision loss in Americans 20 to 74 years old.
Diabetic retinopathy is caused by changes or abnormalities in the
small blood vessels of the retina--changes that take years to occur.
Experts estimate that 6,000 people a year develop retinopathy.
Fortunately, early diagnosis and prompt treatment often can prevent
blindness.
Almost everyone with diabetes develops this complication, but the
first to feel its impact are people with type I diabetes, who frequently
develop a mild form of this condition within five years of diagnosis of
diabetes. In fact, there's a strong correlation between the amount of
time someone has diabetes and the development of retinopathy. Quite
simply, the longer you have diabetes, the greater your chance of
developing retinopathy. Within ten years of diabetes diagnosis, half of
all people with type 1 diabetes and a quarter with type 2 have some
damage to their retinas. By twenty years after diagnosis of diabetes,
nearly everyone with type 1 diabetes and over 60 percent with type 2
have some degree of retinopathy.
Retinopathy is not something to ignore. Among those with type 1
diabetes, retinopathy is responsible for four-fifths of all cases of
blindness: among those with type 2, the number is one-third. Of course,
not all cases of retinopathy result in blindness. The condition ranges
in severity from mild to advanced.
The medical profession describes two forms of diabetic retinopathy:
background retinopathy and proliferative retinopathy. Background
retinopathy is a mild, early form of retinopathy that is characterized
by gradual narrowing or weakening of the small blood vessels in the
eye. Small bulges (called microaneurysms) develop on the vessels.
Eventually a vessel may tear or break and then bleed (known in medical
parlance as a hemorrhage).
Most folks with diabetes develop background retinopathy, but in the
lion's share of the cases, the condition remains at a mild level. Vision
is not affected unless blood vessels break and leak fluid into the
macula, an area of the retina responsible for sharp, fine vision---the
kind of vision needed to read this book. When fluid leaks into the
macula, it swells and puts pressure on other areas of the eye. This
situation is called a macular edema and it leads to blurred vision. The
swelling is sometimes treated in people who appear to be at high risk
for blindness with a high-tech procedure known as photocoagulation. In
this, a precise laser beam is used to sear shut the leaking blood
vessels. Photocoagulation doesn't cure retinopathy, but it can delay the
loss of vision by a number of years or, in some cases, stop
progression.
For the most part, however, because background retinopathy is mild, surgical treatment isn't necessary.
Proliferative retinopathy, as its name suggests, is a severe form of
retinopathy that develops when a network of new, fragile blood vessels
proliferates in the retina at the site of previous breakages or
hemorrhages. The new vessels are an attempt by the eye to repair the
damaged, worn-out vessels caused by diabetes. Over time the new, fragile
vessels may tear and leak blood into the vitreous humor, the clear,
gelatinous material that fills the center of the eye. A small amount of
blood won't dim vision, but the major hemorrhages associated with
proliferative retinopathy may be large enough to affect sight, in which
case they are known as vitreous hemorrhages.
As the eye tries to repair the damage caused by hemorrhages, scar
tissue forms. The buildup of scar tissue may eventually damage the
retina, resulting in partial loss of sight, or it may displace or cause
the retina to become detached, resulting in total loss of vision.
It may be difficult to tell if either form of retinopathy is
developing. For the most part, people can have severe eye damage without
knowing it, because the damage may not affect vision and may cause no
pain. Of course, there are some obvious indications to the person with
diabetes that something has happened to the eye. Partial loss of
vision--even if very small--is an indication of a problem. "Floaters,"
"cobwebs," and "cotton wool balls" are terms that people have used to
describe vision problems caused by tiny hemorrhages in the eye. A
sudden, painful loss of vision may indicate a major hemorrhage.
Naturally, it's best to detect retinopathy before it reaches this
stage. Eye examinations with a tool called a monocular direct
ophthalmoscope are used to detect damage to the retina. A family
physician can perform this test, although several studies indicate that
physicians who are not ophthalmologists detect proliferative retinopathy
in only 50 percent of the people who have the condition. That's not a
particularly encouraging track record--"No better than random chance,"
in the words of one eye expert.
There are some treatment options for those people with advanced
stages of either form of retinopathy: Photocoagulation--the use of laser
beams---can seal leaking retinal blood vessels or reattach a detached
retina. In some people, this is enough to stop the progression of
diabetic retinopathy.
Vitrectomy is another, more intricate surgical procedure used in
people with proliferative retinopathy. In this procedure, a physician
removes the vitreous to clear out the light-blocking hemorrhage, uses
microsurgery to repair the retina, if necessary, and then replaces the
vitreous with a saline solution.
An article in the journal
Annals of International Medicine
explains that photocoagulation and vitrectomy prevent deterioration of
vision in around 60 percent of patients. Laser therapy reportedly
reduces the rate of vision loss by 50 percent in people with
proliferative retinopathy and macular edema, conditions that often
exhibit no symptoms. Vicrectomy reportedly improves visual acuity to
10/20 or better in 36 percent of treated eyes. That's the good news.
However, no surgery is free of potential complications. With
vitrectomy, for example, the overall complication rate is about 25
percent, according to the
Annals of International Medicine
article. Potential complications include infection, cataract
development, bleeding, elevated pressure in the eye (which can lead to a
condition called glaucoma), loss of vision, and retinal detachment or
scarring.
Medical research is also looking at ways of slowing or even
preventing the progression of retinopathy. One small Norwegian study
found that people with type 1 diabetes who maintained near-normal levels
of blood sugar over a long period of time--at least seven years--were
significantly less likely to develop severe retinopathy. The patients in
this study followed a tight-control regimen, using either continuous
subcutaneous infusion pumps or multiple insulin injections.
The results of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial show that
tight blood-sugar control can prevent new cases of retinopathy. Tight
control also helps retinopathy from growing worse, According to the
study, the earlier tight control is instituted, the more beneficial it
is at fending off complications.
Scientists are also hoping to discover why high levels of blood
glucose damage the body's blood vessels. One theory is that an enzyme
called aldose reductase, which converts glucose into a sugar alcohol
called sorbitol, may play a role in triggering diabetic complications.
For that reason researchers are looking into a class of drugs called
aldose reductase inhibitors that block the actions of the enzyme. They
hope these drugs can reduce the chance of developing retinopathy and
other long-term complications. Studies are underway.
In November 1997, the
Journal of the American Medical Association
reported on a number of other agents that may potentially prevent
retinopathy. These include aminoguanidine, a drug that inhibits the
formation of certain proteins and lipids that are thought to contribute
to blood vessel damage. Other possibilities include drugs that interfere
with the growth of blood vessels in the retina; antioxidants such as
vitamin E, thought to prevent damage to the endothelium (the innermost
layer of the cornea, the clear covering of the eye); and agents that
would interfere with the molecular and cellular reactions within the eye
that cause cell death.
Although these new treatments sound promising, the key action in the
here and now is getting prompt medical care for retinopathy,
particularly if you have macular edema or proliferative retinopathy.
Studies have found that there is a 16 percent risk for severe visual
loss if proliferative retinopathy is left untreated for two years. That
may sound like a small risk, but is it really one that's worth taking?
You and your doctor must decide.
There are other ways diabetes can exacerbate retinopathy. Poor
blood-sugar control, high blood pressure, and a history of smoking
increase the risk of retinopathy and increase the chances that the
condition will worsen. And as we mentioned before, people with type 1
diabetes are more likely to develop severe retinopathy.
A woman with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes who has no
retinopathy before pregnancy is unlikely to develop retinopathy during
pregnancy. However, the story is different for women with diabetes who
already have some retinal damage when they become pregnant. About 5 to
12 percent of women with diabetes with mild retinopathy will see their
retinopathy worsen. Women who already have moderate to severe diabetic
retinopathy are at greater risk during pregnancy. In recent studies,
about 47 percent of pregnant women with diabetes had an increase in
severity in retinal damage, and 5 percent developed proliferative
retinopathy.
These rapid changes may be due to the increased levels of hormones
that accompany pregnancy. Pregnancy-induced or chronic high blood
pressure is thought to play a role, too. In one study, 55 percent of
pregnant women with diabetes who had high blood pressure in addition to
retinopathy saw their retinopathy worsen, compared with 25 percent of
the women who had normal blood pressure and retinopathy.
Experts say that pregnant women with signs of retinal damage can slow
the progression of retinopathy by lowering blood-pressure levels.
Doctors have also found that treating a woman's retinopathy with
photocoagulation can help reduce the risk of progression if the laser
treatment is done before she becomes pregnant.
Like anyone with diabetic retinopathy, pregnant women should get
regular eye examinations to monitor the course and development of this
complication.
NEPHROPATHY
Officially known as diabetic nephropathy, nephropathy is a type of
kidney disease that leads to kidney failure. Nephropathy tends to
develop in people who have had diabetes for 20 years or more. It used to
be that a third of all people with type 1 diabetes developed
nephropathy, but today's treatment methods and the emphasis on better
blood-sugar control are shrinking that percentage. People with type 2
diabetes develop nephropathy infrequently.
How It Happens
To see why nephropathy would be a problem, let's look first at what
the kidneys do. The kidneys are organs located near the waist. Inside
the kidneys are small blood vessels, called glomeruli, that act as
filters, removing wastes from the blood and discharging them through the
urine. Useful products, such as protein and glucose, are not eliminated
but are sent back into the bloodstream.
Nephropathy is the condition in which small arteries in the kidneys
become hardened and the glomeruli become damaged, in much the same way
that the small vessels of the eye become damaged during retinopathy. The
kidneys ultimately fail in their job of filtering out wastes. People
with kidney failure must go on dialysis (the use of a machine to filter
blood) or have a kidney transplant; otherwise, lethal levels of wastes
and toxins build up in their bodies.
Nephropathy is caused by high blood-sugar levels. Also, high blood
pressure, arteriosclerosis, smoking, and high cholesterol increase the
likelihood of kidney complications. Frequent urinary tract infections
add to the problem because an infection can easily spread to the kidneys
and damage them.
Recognizing the Signs
Early warning signs of nephropathy include problems emptying the
bladder, blood in the urine, and urinary tract infections. The disease
can be confirmed through simple urine and blood tests. Just as the
kidneys lose their ability to discharge wastes, they also lose their
ability to keep protein and glucose in circulation. Sugar and protein
begin to show up in the urine tests in larger and larger amounts. Blood
tests also detect high levels of urea nitrogen and creatinine, another
indication of kidney damage.
Handling the Problem
To halt kidney damage before kidney failure occurs, the wisest step
is to take urinary tract infections seriously. Remember: Infections can
back up further into the urinary system and spread to the kidneys,
impairing their function.
If signs of developing kidney problems
are detected, doctors often recommend a regimen of tight blood-sugar
control and a low-protein diet to ease stress on the kidneys. Recent
clinical studies suggest that use of the blood-pressure drug enalapril
(Vasotec) may preserve kidney function, but more research is needed to
confirm this.
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
The word cardiovascular means "of the heart and blood vessels."
Cardiovascular complications include problems such as angina, heart
attack, stroke, and others related to poor circulation. Cardiovascular
disease is the most common complication of type 2 diabetes. In fact,
people with diabetes have a risk of cardiovascular disease that is two
to five times that of people without the condition.
How It Happens
Just as diabetes changes the shape of the small blood vessels (known
as microvascular changes), it also appears to thicken and obstruct the
walls of the large blood vessels, thus restricting blood flow. These are
called macrovascular changes. Macrovascular changes (such as
arteriosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries) have been called the
"underlying event" behind most cardiovascular disease. There's no doubt
about it: Cardiovascular complications are very debilitating side
effects of diabetes. However, the risk for such complications can be
decreased by tight blood-sugar control.
Recognizing Risk Factors
Many factors can put a person with diabetes at risk of having a
stroke or heart attack. Just having diabetes increases a person's risk
of experiencing a stroke, according to the American Journal of
Epidemiology, regardless of whether or nor the person has another risk
factor--for example, if he follows a sedentary lifestyle, eats a
high-fat diet, has high blood pressure, or smokes cigarettes. High blood
pressure alone is a major cause of strokes.
Heart attacks and strokes are more common in people with type 2
diabetes than in those with type 1 diabetes, yet medical science is not
sure exactly why this is. Experts believe it could be because people
with type 2 diabetes tend to be overweight. (Obesity is a known risk
factor for heart attack and stroke.)
Cardiovascular complications are, in the general population, more
common in men than in women: Women experience strokes and heart attacks
less frequently than men. Among people with diabetes, however, the men
and women (especially those with type 2 diabetes) have an equal chance
of suffering poor outcomes after heart attacks; they have a much higher
cardiovascular death rate than their nondiabetic peers.
Overall, women seem to have a biological advantage when it comes to
cardiovascular disease--most likely because of the effects of estrogen
in women's systems. However, diabetes appears to be the great equalizer
of the sexes, at least where heart attacks are concerned. Compared with
men without diabetes, men with diabetes have about two times the average
risk of developing cardiovascular disease; women with diabetes have
three to five times the average risk of developing cardiovascular
disease compared with women without the disease.
Handling the Problem
Because the rates of cardiovascular disease are so high in those with
diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends and screening
tests and intervention for heart disease for everyone with diabetes over
age thirty.
Traditional screening tests include having your blood pressure taken
with a blood pressure cuff and having your cholesterol evaluated with a
blood test. An electrocardiogram (EKG) is also recommended. In this
test, electrical leads are placed on the body to measure the electrical
currents of the heart. The currents are then transcribed into a pattern
along a continuous strip of graph paper, which is then read for any
abnormalities.
To prevent heart disease in the first place, you can look to the
obvious tactics of losing weight and lowering blood sugar in addition to
some other methods. For example, if you've paid any attention to
medical news in the past decade, then you should know that lowering
levels of cholesterol and triglycerides is good for your heart.
Cholesterol, a fatlike substance that comes from meat and diary products
and is also produced by the body, is found in all the body's cells and
in. the bloodstream. High levels of cholesterol in the blood, or
hypercholesterolemia, have been implicated in the development of heart
disease in general and arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) in
particular. What you may not know is that people with diabetes tend to
have higher blood-cholesterol levels than other people. They also tend
to have higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), what some call
the "bad cholesterol" because it aids in the deposit of fats on artery
and cell walls. As if that weren't bad enough, people with diabetes tend
to have lower levels of the "good cholesterol," or high-density
lipoprotein (HDL), the substance that escorts excess cholesterol from
the body. All of this is unpleasant news for the cardiovascular system.
Triglycerides (sometimes known is VLDL, or very-low-density
lipoprotein) are another form of fat in the body. High levels of
triglycerides in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia) may not directly cause
arteriosclerosis but may accompany other abnormalities that speed its
development. People with diabetes tend to have high levels of
triglycerides, too. Combine high triglyceride levels of 200 to 500 mg/dl
with cholesterol levels between 200 and 300 mg/dl, and you have what
the American Heart Journal calls combined hyperlipidemia, meaning too
much fat. Triglycerides more than 500 mg/dl and/or cholesterol levels
over 300 mg/dl are called massive hyperlipidemia. Combined and massive
hyperlipidemia are found in over 30 percent of all people with
diabetes--approximately two to three times more often than in people
without diabetes.
We talk more about cholesterol and triglycerides in the next chapter
when we examine diet. For now, it's enough to say that any person with
diabetes who improves his cholesterol picture can help protect against
developing cardiovascular problems. Evidence suggests that for every 1
percent reduction in blood-cholesterol level, there is a 2 percent
reduction in coronary-artery disease for all people, regardless of
whether they have diabetes.
Another thing that people with diabetes can do to reduce their risk
of cardiovascular disease is to pop a simple pill, an aspirin. The
remedy was discovered because a curious thing happened during the course
of a clinical study known as the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy
Study.
Designed to gauge the effects of aspirin on diabetic retinopathy, the
study included 3,700 people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Half took
two aspirins a day (totaling 650 milligrams); the other half took a
placebo. It turned out the aspirin had no effect, positive or negative,
on retinopathy. But something positive did take place: People taking
aspirin were 17 percent less likely to have had a heart attack during
the five years of the study.
Aspirin can't solve all the cardiovascular woes of someone with
diabetes, nor is aspirin useful for everyone. But it would be worth a
trip to the doctor to discuss what aspirin can do for you.
Your doctor may also suggest treatment with drugs such as beta
blockers or ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors--which help
reduce the risk of heart attack in people who already have
cardiovascular disease-or simvastatin, a drug that helps lower
cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of death from heart attack.
NEUROPATHY
Neuropathy is nerve damage. The word "damage" suggests something
irrevocable and permanent, but actually, this is one long-term
complication of diabetes with symptoms that can appear and disappear in a
short period of time. It also varies in intensity, ranging from mild
discomfort to severe, disabling pain.
How It Happens
As is true about many diabetic complications, neuropathy has stumped
medical science when it comes to its causes. It's thought that something
interferes with the body's nerve pathways so that nerve impulses are no
longer transmitted properly. The culprit may be uncontrolled
blood-sugar levels (although many people with good control develop this
complication), or it may be that the nerves are somehow damaged during
the metabolic changes associated with diabetes.
Neuropathy is relatively common. It's estimated that some form of
nerve damage affects 60 to 70 percent of people with diabetes at some
point in their lives. Some physicians claim that it's often the first
noticeable sign of diabetes, particularly type 2. Unfortunately,
neuropathy mimics many other medical conditions (as you'll see in a
moment), so it's often initially diagnosed as something else.
Recognizing the Signs
In general, there are two main forms of neuropathy: peripheral and
autonomic. The most common form of nerve damage, peripheral neuropathy,
is sometimes called sensory neuropathy because it affects nerves that
control sensations in the body. It also affects muscles controlled by
sensory nerves. Sensory neuropathy can weaken muscles in the thighs,
eyes, chest, and abdomen, sometimes causing painful muscle wasting,
double vision and chest pain, More commonly, sensory neuropathy creates
odd sensations (or, in some cases, loss of sensation) in the legs, feet,
and hands. The sensations include numbness, tingling, muscle weakness
and sporadic shooting pains. These sensations can be mild or they can be
annoying. Some people experience double vision for short periods of
time; others have great difficulty walking because of pain or because
they lose some control of leg movements. Neuropathy has been known to
interfere with sleep or rest.
In general, peripheral neuropathy is a temporary condition--one that
disappears as mysteriously as it appears. However, it can lead to injury
in cases where the person with diabetes feels no sensations of pain.
This often happens on the bottoms of the feet, resulting in some of the
foot problems that we discuss shortly.
Autonomic neuropathy is a less common complication, perhaps
experienced by 20 percent of people with diabetes. Autonomic neuropathy
is damage to the nerves that control various bodily functions, such as
the digestive system, urinary tract, and cardiovascular system.
Autonomic neuropathy leads to many inconvenient problems: When it
affects the nerves around the stomach, bladder, and bowels, it can cause
vomiting, constipation, and feelings of bloatedness. When it affects
the nerves that control the contraction of blood vessels, a condition
called orthostatic hypotension may develop. This is a sudden drop in
blood pressure when a person gets up after reclining, which may result
in dizziness or fainting, Impotence, the loss of the ability to have an
erection, is also related to (although not entirely caused by)
neuropathic damage.
Handling the Problem
The symptoms of neuropathy of both types can be treated. Doctors
often prescribe drugs to treat the symptoms of these different
problems----for example, to relax muscles if the problem is
constipation. Exercise helps some people; others benefit from bed rest.
Because neuropathy varies tremendously from person to person, treating
it is often a matter of trial and error.
But though symptoms can be treated, neuropathy itself cannot be
reversed. Medications to treat or prevent nerve damage do not yet exist,
although researchers are conducting studies using aldose reductase
inhibitors-experimental drugs we discussed earlier in relation to
retinopathy.
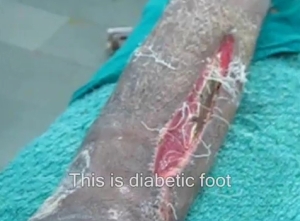
FOOT PROBLEMS
Cardiovascular complications damage blood vessels and diminish blood
flow to the legs and feet. Add damage to the nerves of the legs and feet
through neuropathy, and you've just laid the groundwork for serious
foot ailments.
How They Happen
Foot ailments show up in about half of people who have had diabetes
for 20 years or more. The scenario then proceeds like this: When people
with diabetes lose sensation in their lower legs and feet, they are less
likely to notice damage to the skin and tissues. Such seemingly minor
injuries as cuts, bruises, blisters, bunions, corns, calluses, ingrown
toenails, or even athlete's foot can develop into areas of infected
tissue known as neuropathic ulcers.
It may seem impossible that a blister turns into an ulcer, yet the
process is fairly simple. Let's say you have a new pair of shoes that
has chafed and rubbed one foot raw. The area is red and inflamed. Once
an inflammation or infection begins, its swelling compresses the blood
vessels, which are already damaged or narrowed by diabetes itself. These
factors diminish the flow of blood to the irritated area, meaning fresh
oxygen and infection-fighting blood cells have a more difficult time
getting to the problem site. All of this sets the stage for a serious
infection. Once infection sets in, it's difficult to treat. Antibiotics,
which are carried in the blood, can't reach the infected area
efficiently. About 80 percent of foot ulcers occur on the bottom of
insensate feet, or feet without feeling.
The real danger with the combination of infection and reduced blood
flow is gangrene. If blood flow were to be completely blocked, the cells
served by the obstructed blood vessels would die. Once gangrene sets
in, the only way to stop its spread is by amputation of the dead tissue.
According to an article in Archives of Internal Medicine, "It has
been estimated that the lifetime risk of a lower-extremity amputation is
5 to 15 percent among diabetic individuals, a risk fifteen times that
of the nondiabetic population."
More than half of all lower-limb amputations in the United States are
performed on people with diabetes. Each year, reports the American
Podiatric Medical Association, the number of lower-limb amputations due
to diabetic complications in the United States exceeds the number of
limbs lost worldwide to land mines. Almost half of these 67,000
amputations could have been prevented through early detection and
treatment.
Recognizing Risk Factors
As is true with all diabetic complications, certain factors increase
risk of foot problems. The greatest of these is smoking. According to
the American Diabetes Association, of the people with diabetes who need
amputations, almost all are smokers. Other high-risk factors include
being male and being African-American or Native American. Risk increases
with age, too.
A 1998 study published in the
Archives of Internal Medicine
listed a number of criteria doctors can use to determine a patient's
risk of foot ulcers. These include a history of amputation, diabetes for
more than ten years, existing foot deformities, neuropathy, and
difficulty feeling vibrations with the feet. The study authors
encouraged practitioners to survey for these criteria in order to
prevent such complications.
Handling the Problem
The trick to treating and preventing foot problems lies in finding
out ifs a blood vessel is about to become blocked. It used to be that
doctors could locate blockages in large vessels, such as those of the
legs, only by ordering an x-ray called an angiogram. Then they might
perform bypass surgery to detour blood around the blockage. In this
surgery, a piece of healthy vein is "harvested" from an area of the body
(possibly the thigh) and is attached at either end of the obstruction.
The new vein directs blood to cells that had been receiving an
inadequate supply. It's one method of preventing gangrene-albeit an
invasive and expensive one.
Like many other diabetic complications we have discussed, amputation
doesn't have to happen. With proper foot care, many, if not most,
amputations may well be avoided.
http://www.diabetesinfocenter.org
Apakah penyakit Diabetes bisa disembuhkan??? klik disini..
Bagaimana menyeimbangkan kadar gula darah secara alami??? klik disini...